Ambitious molecules
deserve powerful assays
Our services are designed for researchers from several sectors:
Biotech & Pharma
Powerful mitochondrial assays to predict organ toxicity and assess efficacy of new drug candidates, tests run by an experienced CRO.
Cosmetics
Claim antiaging and slimming properties of ingredients based on competitive testing of mitochondrial fitness and eliminate any compound displaying toxicity.
Chemistry & Agrochemistry
An experienced CRO providing in vitro testing to assess mammalian toxicity of agro- and other chemicals.
Academia
A skilled mitochondrial research partner offering a range of robust assays and personalized studies.

About Mitologics
Since 2009, Mitologics SAS has been tracking and analysing the mitochondrial effects of chemicals or biologics through in vitro testing in healthy and pathological environments. As a CRO, the company performs R&D studies to monitor compound toxicity and efficacy, and advises pharma, biotech, cosmetic, chemistry and agrochemistry companies, as well as academic researchers from all over the world.
News
Testimonial


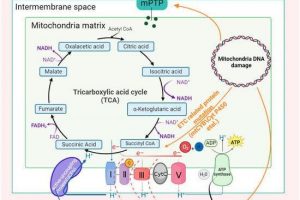
Why focus on mitochondria ?
Mitochondria are the “powerhouse of the cell”; they are essential organelles. By ensuring energy production, cell signalling and ultimately controlling the balance between life and death in eukaryotic cells, they are key players in drug discovery and development, and are also relevant for other sectors, such as cosmetic or chemistry.
Since mitochondria can be harmed by many compounds, examining the mitochondrial safety profile of any new compound during its development is a major checkpoint. In addition, a variety of diseases can be effectively treated by pharmacologically targeting mitochondria as part of innovative therapeutic strategies. The mitochondrion is also a crucial target for cosmetic products aiming to prevent age-related damage.
Mitologics provides services based on in vitro mitochondrial integrity and functionality assays.